
Dynamics

|
Generational Dynamics |
| Forecasting America's Destiny ... and the World's | |
| HOME WEB LOG COUNTRY WIKI COMMENT FORUM DOWNLOADS ABOUT | |
| Place and time | Tuesday, April 20, 2004, 6:00 pm, MIT e-club meeting, 56-114 (click here for map). Contact: Richard Shyduroff, 207-230-0465, mailto:rdshydur@mid.edu |
|---|---|
| Speaker | John J. Xenakis, MIT Class of '65 and "all but thesis" for Ph.D (Mathematics - Course 18), author of Generational Dynamics: Forecasting America's Destiny, phone: 508-875-4266, e-mail: mailto:john@GenerationalDynamics.com, web site: http://www.GenerationalDynamics.com |
|
|
 |
A methodology for understanding history |
| - | Generational cycles - length of a human lifespan |
| - | Principle of localization |
| - | How wars begin |
| - | Crisis wars versus non-crisis (mid-cycle) wars |
| - | How smalls wars either extinguish or expand |
| - | How one major war cycles to the next major war |
 |
A methodology for forecasting history |
| - | Restriction: Can only make forecasts that depend on (generational) changes in attitudes and beliefs of large masses of people |
| - | Politics, culture, tastes, economics, international finance |
|
 |
Public sector |
| - | Foreign policymaking - CIA, State Dept. |
| - | Military planning |
 |
Private sector |
| - | Multinational marketing and corporate management |
| - | International investments |
| - | Polling (survey) models |
|
 |
|
 |
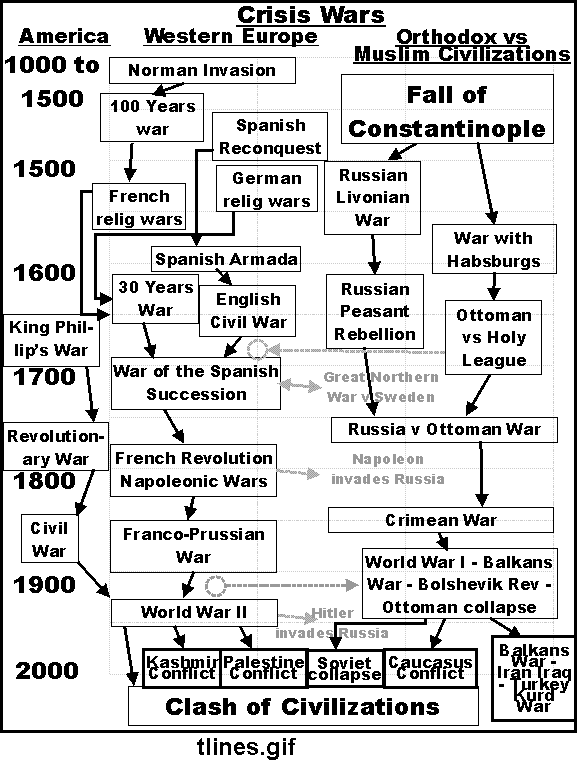
Crisis Wars |
| - | Rwandan War - 1994 |
| - | Balkan War - early 1990s |
| - | Cambodian killing fields - 1970s |
| - | World War II |
| - | 70-90 year cycle |
 |
Mid-Cycle Wars |
| - | World War I |
| - | Vietnam War |
|
 |
Crisis War Characteristics |
| - | Visceral cause - fury, fear that nation in danger |
| - | High energy: preparation, pursuit, revenge |
| - | Bottom-up - effort driven by the people |
| - | Minor anti-war (pacifist) movement |
| - | Targeting civilians - genocidal |
| - | Outcome: Major political, structural, boundary changes |
 |
Mid-cycle War Characteristics |
| - | Political cause |
| - | Low energy: surprise, defense, revanche |
| - | Top-down - Effort driven by the political leaders |
| - | Dominant anti-war (pacifist) movement |
| - | Political protection of civilians |
| - | Outcome: Little real change; "Internal revolution" |
 |
Sex and Genocidal Crisis Wars |
| - | Both are human needs |
| - | Both are irrational |
| - | Both occur regularly |
| - | Both are essential to survival of the fittest |
| - | Sex increases population, genocidal war selectively reduces population |
|
 |
|
 |
 |
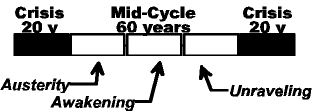
From 'austerity' to 'awakening' |
| - | Only one generation past Iran/Iraq war, 1980s |
| - | Civil war is almost impossible (99%) |
 |
Terrorist acts |
| - | Actions of individuals and small groups |
| - | Possible 'Tet offensive' near June 30 |
 |
|
 |
 |
Like Iraq - Only one generation past Iran/Iran war, 1980s |
 |
Pro-American riots and demonstrations since 1999 - overthrow mullahs? |
 |
Is Iran developing nuclear weapons? |
|
 |
Palestinian Arabs vs Iraqi Muslims |
| - | "If provoked they'll start a war, but if we're careful they won't" |
| - | Different places in generational cycle |
 |
Recent history |
| - | Replaying 1936-1949 |
| - | Ariel Sharon versus Yasser Arafat |
 |
From 'unraveling' to 'crisis' |
| - | Sharon's Disengagement - Wall |
| - | Assassination of Hamas leader Sheikh Ahmed Yassin |
| - | Suicide bombings as moderation |
| - | Regional war almost mathematically certain (99%) |
 |
|
 |
Early history of Haiti |
|
| - | 1492 - Christopher Columbus discovers Hispaniola |
| - | 1700s - Wealthy French colony - 500K slaves |
 |
Market-dominant minority vs majority |
| - | French-speaking light-skinned mulattos, mixed blood |
| - | Creole-speaking blacks (noirs) - 95% of pop |
 |
Massacres in twentieth century |
| - | 1915 - Crisis civil war |
| - | 1915-34 - American occupation |
| - | 1937 - Massacre by Dominican Republic's Trujilo |
| - | 1960s - Massacre by Dr. Francois Duvalier |
 |
Today's crisis period - 1992 to present |
| - | Malthus effect - food becomes more expensive |
| - | War postponed by money infusion |
| - | Analyst predictions: Occupation for 20 years |
|
 |
 |
Korean vs German Unification |
| - | Both partitioned after World War II |
| - | Different places in generational cycle |
| - | Korean war (1950-53) armistice after stalemate |
 |
Impending reunification war |
| - | Kim Jong-il: "Embargo means war" |
| - | South Korean youth: Blaming America for partitioning |
|
 |
 |
1853-68 - Commodore Perry to Meiji Restoration |
| - | Change in national character ('national lobotomy') |
| - | 1894-1910 - Imperialist wars with China and Russia |
| - | Won Taiwan, Korea, southern Manchuria |
 |
1930-45 - World War II |
| - | 1930 - Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act |
| - | 1931 - Invade Manchuria |
| - | US / League of Nations oil embargo |
| - | Invade China |
| - | 1941 - Bombs Pearl Harbor |
| - | Becomes pacifist nation |
|
 |
 |
History of rebellions |
| - | 1796 - White Lotus Rebellion |
| - | 1851-71 - Taiping Rebellion and others |
| - | Population: 410 million to 350 million |
| - | 1934-49 - Mao's Long March, crisis civil war |
| - | 1949 - Chiang Kai-shek flees to Taiwan |
 |
The Miserable Generation ('Baby boomers') |
| - | 1950s -- All lawyers executed |
| - | 1958-60 Great Leap Forward - 10s M deaths |
| - | 1966-76 Cultural Revolution - indoctrination |
 |
Awakening to Unraveling |
| - | 1989 - Tiananmen Square massacre |
| - | 1992 - Birth of Falun Gong |
| - | 2000 - Over 100 million adherents of Falun Gong |
 |
Unraveling to Crisis |
| - | Income disparity - rural peasants vs city workers |
| - | Collapse of Mao's structure - migration to city |
| - | Financial bubble |
| - | Taiwan reunification crisis |
|
 |
 |
"Wild Lily" generation |
| - | Wild Lily rebellion - 1990 |
| - | Develop Taiwanese (vs Chinese) identity |
| - | 2000: Election of Chen Shui-bian from Democratic Progressive Party |
| - | Moving away from China |
|
 |
 |
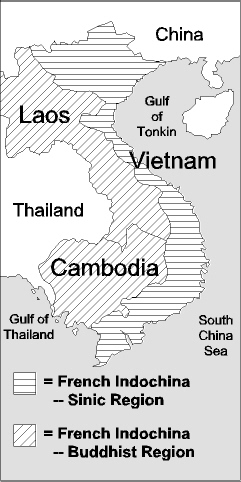
French Indochina |
| - | 1882-93 Crisis war between France and China |
| - | 1954 French driven out by Ho Chi Minh |
 |
Vietnam War - 1965-75 |
| - | Crisis war for Vietnam |
| - | Mid-cycle war for America |
 |
Cambodia / Laos Civil War |
| - | Crisis civil war |
| - | Massive genocide and starvation (killing fields) |
 |
|
 |
American Crisis Wars |
 |
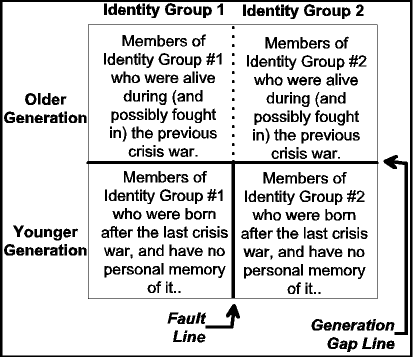
Identity groups, fault lines, crisis wars |
 |
Generation gaps versus fault lines |
 |
Judaism, lives of Jesus and Mohammed |
|
 |
Changes since 9/11 |
| - | Visceral fear and anxiety - way of life in danger |
| - | Fury at Islamic terrorists - revenge vs revanche |
| - | Willingness to lock up Muslims with little or no probable cause (like Japanese during WW II) |
| - | CIA and FBI - merging databases |
| - | Increase patriotism |
| - | Pre-emptive foreign policy |
 |
Europe after Madrid 3/11 |
 |
Generational change around year 2000 |
 |
Political shifts |
| - | Gender gap and gender wars nearly extinguished |
| - | Christian right / Jewish left: common goal of defending Israel |
| - | Democrats need to focus on economy, not bash Bush on war |
|
 |
Crisis Wars in American History |
| - | 1670-90 King Philip's War Crisis |
| - | 1772-90 Revolutionary War Crisis |
| - | 1857-1870 Civil War Crisis |
| - | 1929-1945 World War II Crisis |
 |
Mid-Cycle (Interim) Wars |
| - | 1846-48 Mexican War |
| - | 1898 Spanish-American War |
| - | 1917-18 World War I |
| - | 1950-53 Korean War |
| - | 1964-73 Vietnam War |
| - | 1991 Persian Gulf War |
|
 |
World War II was a crisis war |
| - | No hesitation after Pearl Harbor |
| - | Antiwar (pacifist) movement fizzled |
| - | Loss of individual rights - confinement |
| - | No protection for civilians |
| - | Visceral fear and fury |
| - | Desire for revenge (vs. revanche) |
 |
World War I was a mid-cycle war |
| - | Christmas Truce (England/Germany, 1914) |
| - | American neutrality till 1917 - despite terrorism |
| - | Strong anti-war (pacifist) movement in America |
| - | Unnecessary German capitulation |
| - | Crisis war for Russia and Ottoman Empire |
 |
Vietnam War was a mid-cycle war |
| - | Generation gap - G.I. generation v Baby Boomers |
| - | Strong anti-war (pacifist) movement in America |
| - | Protection of civilians |
| - | Crisis war for Vietnamese |
|
 |
Major Civilizations of the World |
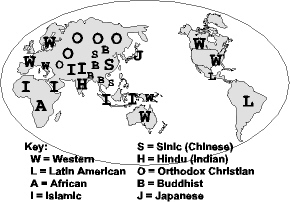 |
| - | Western, Latin American, African, Islamic, Sinic (Chinese), Hindu, Orthodox, Buddhist, and Japanese |
 |
Identity groups |
| - | Bosnian war: Serbs vs Bosnians vs Croats |
| - | Orthodox Christians vs Muslims vs Western Christians |
 |
Fault lines |
| - | France vs Germany |
| - | Western vs Orthodox Christianity |
| - | Islam vs Orthodox Christianity |
|
 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Cause of war vs Timing of war |
|
| |||||||
|
| |||||||
|
 |
|
 |
A Diaspora religion |
| - | 1200BC Exodus: Hebrews under Moses cross Red Sea out of Egyptian slavery and survive in the desert |
| - | 500BC Jews exiled into Babylon, return to Jerusalem |
| - | Jews could live anywhere, without a homeland, and maintain a Jewish identity |
| - | ..................... To be completed ....... |
|
 |
Life of Jesus |
| - | 4 BC - Born at end of crisis period |
| - | Became popular during awakening period |
| - | Did not flee when threatened with death because of Isaiah |
| - | 66AD - Destruction of Jerusalem - spread of Christianity |
 |
Life of Mohammed |
| - | 570 AD - Born at beginning of crisis war - orphaned |
| - | Became popular during awakening period |
| - | Fled from Mecca to Medina when threatened with death |
| - | 630 Conquered Mecca ten years later, died several years later |
| - | 665 - Crisis civil war among followers - spread of Islam |
 |
Awakening periods |
| - | The time when great ideas are born |
| - | Great ideas extinguish or spread during next crisis war |
| - | Name comes from "The Great Awakening" - period of 1730-40s - when multiple religions spread on American east coast |
|
 |
Eastern Europe is NOT like Western Europe |
 |
Orthodox Christianity is NOT like Western Christianity |
|
|
|
|
 |
The most remarkable warrior in world history |
 |
Spread Greek culture and language through the entire region |
|
|
 |
In 285, administratively split into easter and western region |
 |
Western Roman Empire collapsed in 476 |
|
 |
 |
Byzantine Empire the last remnant of Roman Empire |
| - | Roman Empire in the West had been destroyed |
| - | Centered in city of Byzantium, later called Constantinople |
| - | Pope and Catholicism remained in the West |
| - | Catholic religion became stateless |
| - | Major doctrinal differences developed |
| - | Orthodox churches still exist in Africa today |
|
|
 |
Islam spread like wildfire |
 |
Doctrinal issues: Quran vs Sunna |
| - | Sunna are habitual behaviors, published long after death |
| - | Split in Sunnism vs Shi'ism |
|
|
 |
In 1000, both Islam and Orthodox Christianity were threatened with extinction |
 |
Seljuk Turks from Central Asia adopted Islam |
| - | 988 - Vladimar adopted Orthodox Christianity for Slavs |
 |
Catholics sack Constantinople in 1204 |
 |
Slavs moved east and formed Russian Empire |
|
|
 |
Rise of Ottoman Empire |
| - | 1300 - Turkish Muslim tribal chief Osman started to expand |
| - | 1453 - Fall of Constantinople - renamed Istanbul |
 |
Russia assumes a new role |
| - | Moscow took on the mantle of the true heir to the Roman Empire |
| - | Russian leader is Tsar (or Czar) named after Caesar |
| - | Tsar is also head of the true ("Orthodox") Christian Church |
| - | Tsar is also protector of Jerusalem |
| - | Orthodox Christianity is not a stateless religion |
 |
Russia vs Ottoman Crisis Wars |
| - | Russian war with Ottomans, 1672-83 |
| - | Crimean War, 1850s |
| - | World War I, 1910s |
|
 |
Triggered by crisis war in the Balkans in 1910s |
| - | Germany pulled into war because of treaty with Austria |
| - | Balkans war replayed in the 1990s |
 |
Bolshevik Revolution, 1917 |
| - | Russia abandons role in World War I |
| - | Communist state -- repudiation of Tsarist government |
| - | Godless state - repudiation of Russian Orthodox Church |
| - | Repudiation of role as protector of Jerusalem |
| - | Stalin/Trotsky civil war - tens of millions murdered |
 |
Collapse of Ottoman Empire |
| - | Young Turks - Rise of Turkish identity (vs Ottoman identity) |
| - | Armenian genocide |
| - | Abolition of the Sunni Muslim Caliphate |
| - | Rise of Arab identity |
 |
Rise of Zionism |
| - | 1917 - Balfour declaration calls for state of Israel |
| - | 1930s - Nazi persecution - Jewish migration to Palestine |
| - | 1936 - Jewish-Arab conflict begins |
| - | 1948 - Partitioning of Palestine - state of Israel - full scale regional crisis war |
|
|
 |
Fault line conflict regions |
| - | Balkans |
| - | Crimea |
| - | Caucasus (Chechnya) |
| - | Uzbekistan (to right) |
|
 |
|
 |
Global technology cycles - Kondratieff cycles |
 |
Generational cycles and bubbles |
 |
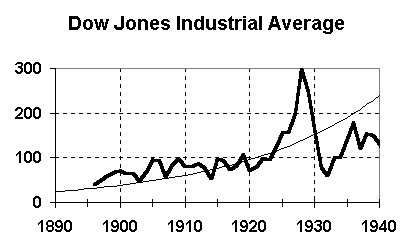
A new "Great Depression" |
|
 |
 |
Characteristics of 1930s Great Depression |
| - | Big credit bubble in 1920s - borrowed money to bid up stock prices |
| - | Nobody knew what was going on until a month into stock market crash |
| - | 1920s stock market bubble CAUSED the 1930s Great Depression |
| - | Establishment of SEC and stock market regulations specifically designed to prevent another credit bubble |
 |
1929 collapse |
| - | Stock market became increasingly volatile |
| - | Below a certain level hit a 'tipping point' |
| - | People forced to sell to meet margin credit requirements |
 |
Previous big credit bubbles |
| - | Panic of 1857 (prior to Civil War) |
| - | British banking failure in 1772 |
|
 |
 |
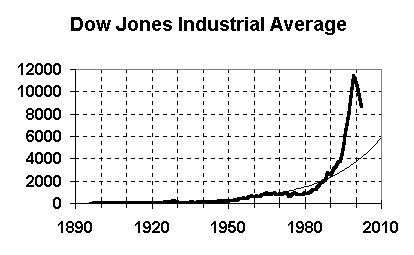
New 1990s credit bubble (using stock options) |
 |
Complete failure of SEC and stock market regs |
 |
Trend line (exponential) |
| - | Current (early 2003) value: Above 10000 |
| - | Trend value in 2010: 5800 |
| - | Predicts fall to around 4000 in next few years |
|
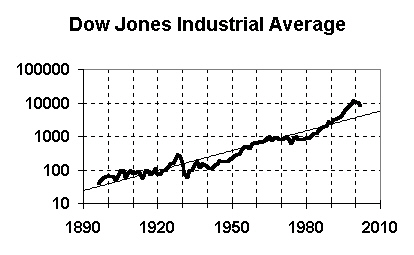 |
 |
Graph now shows both credit bubbles |
|
 |
 |
For those who consider the DJIA to be too artificial |
 |
Trend line (exponential) |
| - | Current (early 2003) value: Above 1100 |
| - | Trend value in 2010: 589 |
| - | Predicts fall to around 400 in next few years |
|
 |
 |
P/E Ratio measures price of stock vs historical earnings |
| - | Historical average around 13 |
| - | Above 18: Stocks are expensive |
| - | Below 10: Stocks are inexpensive |
| - | Historically goes below 10 after exceeding 20 |
| - | Predicts stock market fall of 50% or more |
|
 |
Credit bubbles every 70-90 years (generational cycle) during 'unraveling' period |
| - | Credit bubble / depression creates a risk-aversive generation |
| - | New bubble when previous risk-aversive generation retires |
| - | Financial crisis and war crisis reinforce each other |
 |
"Crusty Old Bureaucracy" theory |
| - | Informal (not rigorous) explanation |
| - | Every organization becomes bureaucratic in time - bankruptcy |
| - | Same rules applies to entire nation in 70-90 year cycles |
|
 |
Greenspan in 1997 |
| - | Had referred to "irrational exuberance" |
| - | Knew that a stock market bubble was forming |
| - | Decided to deal with consequences rather than end bubble |
 |
Federal Reserve after 2000 |
| - | Prevent 1929 forced selling 'tipping point' |
| - | Reduced interest rates (overnight funds rate) to 1% |
 |
Consequences of low interest rate |
| - | Housing bubble |
| - | High auto sales |
| - | Increased personal borrowing during unemployment |
| - | Extension of stock market bubble |
 |
Medium range risks |
| - | Collapse of Chinese credit bubble |
| - | Oil disruption through Mideast war |
| - | Loss of confidence after terrorist attack |
| - | Cyclic downturn spiraling down |
|
|
 |
Identifying technology cycles |
| - | Smooth the S&P index, ignoring bubbles |
| - | Cycle length 40-50 years |
| - | Technology (Kondratieff) cycles have been identified for hundreds of years |
 |
Technology versus Generational cycles |
| - | Technology cycles are global, generational cycles are local |
| - | Entirely independent - can enhance or cancel each other |
|
 |
Goes beyond timing of wars |
 |
This work is in progress, subject to change |
|
 |
Recognizing the visceral causes |
| - | Mid-cycle wars are political - top-down - reasoning |
| - | Crisis wars are visceral, instinctive, unreasoning, emotional |
| - | Visceral motivations occur once every 70-90 year cycle |
 |
Signs of visceral hatred |
| - | Genocide, mass murder, mass rape, rape with bottles |
| - | Desire for vengeance |
| - | Fear that nation or way of life is in danger |
|
 |
Isolating causes of visceral fears |
| - | Example: Americans after 9/11 vs London 1943 |
| - | Example: Causes of American Civil War |
| - | Visceral fears arise only in generational crisis periods |
 |
Threats lead to visceral fears |
| - | Threat of invasion |
| - | Threat of terrorism |
| - | Threat of starvation |
| - | Threat of disease (e.g., black plague) |
| - | Threat of internal insurrection |
| - | Threat of government violence |
| - | Perception of threat may be irrational (crisis periods) |
| - | Applies to large masses of people during crisis periods |
|
 |
Provoking visceral fears |
| - | Applies to large masses of people during crisis periods |
| - | Surprise terrorist attack |
| - | Assassination |
| - | Outbreak of disease |
| - | Sudden increase in price of food or rent or taxes |
| - | Sudden loss of job or income |
| - | Tariff law or oil embargo causing unemployment |
| - | Note: That's why even non-violent acts can be thought of as acts of war |
 |
Visceral fear -> Visceral hatred -> War |
| - | 'Enemy' executes hostile surprise - violent or non-violent |
| - | Feel visceral fear - may be irrational |
| - | Determine threat causing visceral fear - may be irrational |
| - | Assign cause or fault to threat as 'enemy' - may be irrational |
| - | Population develops feelings of fear and fury |
| - | Triggers "them or us" feelings |
| - | Leads to war |
|
 |
Yale Professor Amy Chua in World on Fire |
 |
Example: 1994 Rwanda genocide |
| - | Tutsis (14% of population) - market-dominant minority |
| - | Hutu (85% of population) |
| - | In 1994, Hutus hacked to death 900K Tutsis in 3 months |
 |
Other examples |
| - | Chinese are MDM in many countries throughout Southeast Asia |
| - | Whites are MDM in South Africa |
| - | Lebanese are MDM in West Africa |
| - | Ibo are MDM in Nigeria |
| - | Jews are MDM in post-Communist Russia |
|
 |
Essay on Population, published in 1798 |
| - | Population grows geometrically |
| - | Food supply grows linearly |
| - | Therefore population will always outstrip food supply |
 |
Corrected rates |
| - | Population grows exponentially |
| - | Food supply grows exponentially, at a slower rate than population |
| - | Therefore population will always outstrip food supply |
| - | This applies both regionally and globally |
 |
My own estimates |
| - | Food supply grows at .96% per year, based on USDA wheat yields since 1860 |
| - | Population grows by 1.29% per year, based on UN estimates |
| - | Population grows by 3-5% in some countries, based on CIA Fact Book |
|
 |
Nature's methods for reducing population |
| - | Famine, disease, war |
| - | 20-40 wars on any day in any year |
| - | Major method is war, not famine |
 |
The Malthus Effect - my phrase for how food scarcity leads to crisis war |
| - | As time goes on, population grows faster than food supply |
| - | As time goes on, food becomes relatively scarcer |
| - | As time goes on, price of food goes up |
| - | Bowl of rice costs 1 hour labor -> 2 hours -> 3 hours |
| - | Poverty and starvation lead to humiliation and hatred |
 |
Malthus Effect during non-crisis periods |
| - | Poverty and starvation lead to looting and low-level violence |
| - | Low-level violence handled by standard police methods |
| - | Mid-cycle problems handled with restraint: compromise and containment |
 |
Malthus Effect during crisis periods |
| - | Looting and low-level violence provoke visceral fears |
| - | Both sides overreact |
| - | Looting leads to brinkmanship and increasing demands |
| - | Reactions involve increased violence and higher visibility |
| - | Ping-pong hostile surprises lead to war |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
 |
Additional theoretical development |
 |
Development of predictive "World Model" |