|
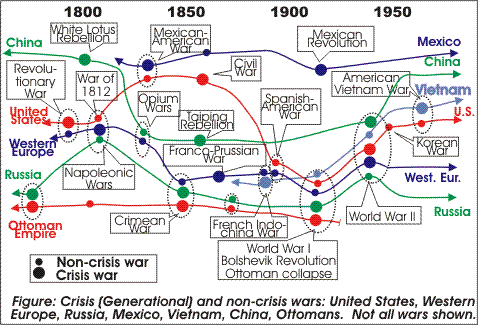
The previous discussion shows how certain types of wars, crisis wars, follow a cyclic pattern. We previously discussed this graphic:
 |
The dots in this graphic represent crisis and non-crisis wars. If you remove the timelines and just look at the dots, then then there's no apparent pattern. But if you follow the timeline for each country, then you see that the crisis wars cycle at approximately 70-90 year intervals, the length of a maximum human lifespan.
The intuitive explanation for the crisis war cycle is this: Crisis wars are the most vengeful, furious, raging and genocidal wars that any nation pursues. A new crisis war only begins roughly when the last generation of people who lived through the last crisis war, and have personal memory of it, are gone (retire or die).
We now turn to the theory that expands this intuitive explanation into a detail theory of the flow of generations.
The Generational Dynamics theory is derived from work done by historians William Strauss and Neil Howe in the 1980s and early 1990s.
Their work is documented in two books, Generations: The History of America's Future, 1584 to 2069 and The Fourth Turning: An American Prophecy.
Strauss and Howe's work develops a generational theory that applies to what they call "the Anglo-American timeline," described in The Fourth Turning.
The Generational Dynamics theory is derived from the Fourth Turning theory, and produces nearly identical results for the times and places that the Fourth Turning covers -- Anglo-Saxon periods since the War of the Roses. The phrase "fourth turning" refers to a crisis period, an approximately 20-year period in which a crisis war occurs. Thus, a "fourth turning" and "crisis war" can be considered to be roughly equivalent.
In order to expand The Fourth Turning so that it applies beyond the Anglo-American timeline restriction, it's been necessary to modify and expand it in a number of ways. The resulting Generational Dynamics theory applies to all nations at all times.
In the following sections, we'll summarize the the Strauss and Howe theory, and we'll explain where Generational Dynamics differs.
I'll use these abbreviations:
&& ***** Summary of The Fourth Turning theory
The Fourth Turning (TFT) theory is based on work that William Strauss and Neil Howe began in the 1980s. They noticed that people differed dramatically based on what generation they were in. The found that people who fought in World War II were quite different from people who were raised during World War II, and that those were quite different those who grew up after World War II. The similarities among people in the same generation outweighed the individual differences, and the differences between people in different generations were usually enormous compared to differences between individuals in the same generation.
They were not the first to notice that one generation differs from another, of course. The popular press regularly labels generations with such names a "Generation X," "Generation Y," "Baby Boomers," and so forth, and many articles are published discussing the characteristics of one generation versus another.
For example, the babies born in the 1930s and 1940s were originally called "depression babies," but in the 1950s, Time Magazine gave them a new name: the Silent Generation, because they valued conformity and loyalty above all else, and didn't complain about much.
The members of the Silent Generation were too young to fight in World War II, so they lived in the shadow of the G.I. Generation, their older brothers and sisters who became heroes who actually fought in the war, and are now called by Tom Brokaw and others "the greatest generation of the 20th century."
Meanwhile, the Silents had to deal with a new generation, the Baby Boomers who were born after the war. The Boomers were very sure of themselves, and led the antiwar riots and demonstrations during the 1960s and 1970s, rebelling against their parents in the G.I. Generation. The Silents were sandwiched between these two warring generations, and served as mediators and compromisers.
&&3 Identifying generational and archetypes
Strauss and Howe embarked on a project to read histories and diaries written throughout American history, passing through colonial times, going back to the original English settlers.
Reading these histories and diaries, they came to a startling conclusion: That generations following historical "fourth turnings" or "crisis wars" following the pattern as generations following World War II, and that the sequence of these generations leads to the next crisis war.
The TFT authors identified four distinct generational types that are repeated over and over, and are similar to the generations they had studied.
The four generations are as follows:
These generational arechetypes were found by the authoris when they read several centuries of histories and diaries. They were surprised to find that these types cycled.
&&3 Generational eras - the four Turnings
Corresponding to the four generational archetypes are four eras or "turnings" through which a society cycles. These are as follows:
The authors describe this period as follows: "An Awakening is an era of cultural upheaval and spiritual renewal. It begins when the waxing social discipline of the High suddenly seems tiresome, unfulfilling, illegitimate, and unjust -- and when people begin to defy it in the name of spiritual authenticity. By now, memories of the last Crisis are buffered by the High's calm and comfort, and the core High virtues are regarded as outmoded, even unnecessary. The Awakening climaxes just after civilized progress reaches a saecular high tide -- and just before that progress is overwhelmed by the liberating passions of reform and protest. The Awakening ends when the new consciousness converts its enemies and the new values regime overwhelms its oppressors."
The authors describe the relationships of these eras as follows: "Like the four seasons of nature, the four turnings of history are equally necessary and important. Awakenings and Crises are the saecular solstices, summer and winter, each a solution to a challenge posed by the other. Highs and Unravelings are the saecular equinoxes, spring and autumn, each coursing a path directionally opposed to the other. When a society moves into an Awakening or Crisis, the new mood announces itself as a sudden turn in social direction. An Awakening begins when events trigger a revolution in the culture, a Crisis when events trigger an upheaval in public life. A High or Unraveling announces itself as a sudden consolidation of the new direction. A High begins when society perceives that the basic issues of the prior Crisis have been resolved, leaving a new civic regime firmly in place. An Unraveling begins with the perception that the Awakening has been resolved, leaving a new cultural mindset in place."
&&2 TFT's Diagonal Diagram: How one generation flows to next
The Fourth Turning (TFT) defines four generation archetypes and four eras or "turnings." The personality of a person in each generation is determined by the era in which that person is born. (Actually, children born two to five years before the start of an era are considered part of that era.)
Thus, the generations determine the eras, and the eras determine the generations.
The relationships between the generational archetypes and the turnings is summarized by the following diagram:
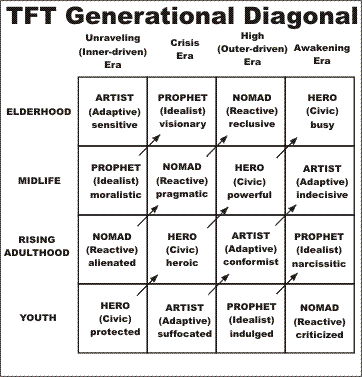 |
This diagram summarizes the TFT generational model: History proceeds in a continuing flow of generational changes, cycling back to the beginning with a cycle length of 70-90 years, the approximate maximum length of a human lifespan.
&&2 TFT's Six Anglo-American Crisis Events (Fourth Turnings)
TFT's Diagonal Diagram summarizes a complex model that purports to describe how the world works. Does the world really work that way? The TFT authors say that it does for Anglo-American history dating back to the 1400s.
The book The Fourth Turning provides detailed evidence, based on reading hundreds of contemporary diaries and histories, that the TFT model works for that period.
TFT describes each turning in detail, and each generation in detail, and how they conform to the TFT model. This information is provided in detail in their two books, and here we can do no more than provide the barest summary of the events covered.
The following are the six fourth turning crisis events described by TFT:
TFT shows how each of these crises leads to the next one. However, the Civil War represents an exception that doesn't satisfy the model, as we'll describe.
&&2 TFT's Six Spiritual Awakening Periods (Second Turnings)
Just as important to The Fourth Turning (TFT) model as the fourth turning crises are the second turning spiritual awakenings that occur midway between two crises. The most recent American awakening period was the 1960s, which saw the racial equality movement, the antiwar movement, the women's lib movement and the environmental movement.
TFT describes both a crisis and an awakening period as "a social moment," which is "an era, typically lasting about a decade, when people perceive that historic events are radically altering their social environment." The difference between the two kinds of social moments are that crisis periods secular crisis and awakening periods are episodes of widespread and tumultuous spiritual fervor.
As described in the authors' book Generations, several social and religious historians since the 1970s have explored the importance of these episodes.
The authors specify six awakenings, corresponding to the six crisis periods identified above, and following the crisis period by several decades. The last five of the six correspond to awakenings specified by the McLoughlin book referenced above.
&&2 Limitations and restrictions in the TFT model ..........
... list restrictions
Many of the elements of TFT are very hard to verify because of inherent ambiguities and uncertainties. For example, how do we evaluate whether a particular generation is "Civic" or "Idealist"? The ambiguity arises from the fact that some people in any generation will be "civic," and some will be "idealist." The uncertainties arise because there's no way to determine any information of this sort for many periods in history, because of the lack of written records.